Cn swimming pools operating. Water supply and sewerage
SYSTEM OF REGULATORY DOCUMENTS IN CONSTRUCTION
CODE OF RULES FOR DESIGN
AND CONSTRUCTION
SWIMMING POOLS
SP 31-113-2004
Moscow
2005
FOREWORD
1. DEVELOPED by the St. Petersburg State Academy of Physical Culture. P.F. Lesgaft (SPb. GAFC) of Rossport and the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Scientific and Design Institute of Educational, Commercial and Leisure Buildings" (Institute of Public Buildings) as part of the implementation of paragraph 17 of the activities of the subprogram " Physical education and health improvement of children, adolescents and youth in Russian Federation(2002 - 2005)" of the federal target program "Youth of Russia (2001 - 2005)"
2. INTRODUCED by the St. Petersburg State Academy of Physical Culture. P.F. Lesgaft
3. REPRESENTED by the Department of Architecture and the Department of Standardization, Technical Regulation and Certification of the Gosstroy of Russia
4. APPROVED by orders of the rector of the St. Petersburg State Academy of Physical Culture. P.F. Lesgaft dated February 9, 2005 No. 25 and director of the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Institute of Public Buildings" dated April 23, 2004 No. 11
5. APPROVED AND RECOMMENDED for use as a regulatory document in construction by the letter of the Gosstroy of Russia on April 30, 2004 No. LB-322/9 and the Federal Agency for Physical Culture, Sports and Tourism by Order No. 24 of February 26, 2005.
INTRODUCED FOR THE FIRST TIME
INTRODUCTION 1 area of use 3 General 4 Parameters and equipment of pool baths 4.1 Sports baths 4.2 Baths for physical culture and health activities 4.3 Baths for disabled people 5 Dressing rooms 6 Ancillary facilities 7 Structures and decoration of rooms with damp and wet conditions 8 Natural light 9 Acoustics 10 Water supply and sewerage 11 Heating and ventilation 12 Automatic and sound equipment of pool baths 13 Power supply and electrical devices Annex ASet of premises in the pool according to the criteria of need Annex B Composition of the premises of medical rehabilitation centers Application Illustrations |
INTRODUCTION
The development of the system of sports and health facilities in our country is becoming increasingly important. At the same time, there is a need to ensure the availability of health and sports activities for all age groups of the population, both healthy people and disabled people.
The regulatory document was developed in accordance with the State contract with Rossport No. 209 dated December 10, 2002 within the framework of the subprogram "Physical education and rehabilitation of children, adolescents and youth in the Russian Federation (2002-2005)", clause 17 "Development of architectural and planning standards for their application in the construction of sports and recreation and sports facilities, taking into account the possibility of their use by disabled children.
The set of rules is made in the development of SNiP 2.08.02-89 * "Public buildings and structures" and is a document federal level. It deals with the functional and technological requirements for the design of pool baths for sports and leisure activities, available for sports and recreational activities. The document was developed taking into account the requirements for baths and pool rooms, reflected in the rules of the competition, based on the design experience and practice of operating pools for various purposes.
When developing this Code of Rules, the following conditions for organizing the spatial environment in buildings and premises were taken into account:
dimensions of a person and groups of people in various positions, taking into account the characteristics of different age groups of healthy people and disabled people;
functional and technological (sports) processes associated with individual physiological and social functions of a person, as well as with the operation of simulators, equipment and the use of inventory;
requirements for acoustics, soundproofing of halls;
norms of natural and artificial illumination of premises, frequency of air exchange, etc.;
quality and frequency of water exchange in pool baths;
The following materials are partially used in the text and graphic part of the Code of Rules:
Pool Design (Reference Guide to SNiP 2.08.02-89). - M.: Stroyizdat, 1991.
Normals of planning elements of residential and public buildings:
Issue NP 5.3.2-76 Auxiliary premises of sports facilities. Moscow: Stroyizdat, 1976.
Issue 12. Public buildings and structures. Athletic facilities. - M.: GUP TsPP, 1999.
Physical culture and sports facilities / Ed. L.V. Aristova. - M.: Sport Academ Press, 1999.
Aristova L.V. Physical culture and sports facilities for the disabled: Textbook. - M.: Soviet sport, 2002.
Yasny G.V. Sports pools. - M.: Stroyizdat, 1988.
The set of rules "Pools for swimming" was developed by a scientific and creative team led by L. V. Aristova, professor of St. Petersburg. GAFC them. P.F. Lesgaft.
Authors of SP 31-113: responsible executors - Ph.D. economy Sciences L.V. Aristova, Ph.D. archit. A.M. Garnets (Institute of Public Buildings), architect. SOUTH. Zhura (VNI-IFK), Ph.D. archit. B.P. Anisimov (Institute of Public Buildings) with the participation of Ing. B.A. Arutyunova (Russian Association of Sports Facilities).
(Revised edition, Amendment 10.2006)
Scientific editor - Ph.D. archit. A.M. Garnets.
Computer graphics - archit. K.V. Karpacz (TsNIIEP housing), Ph.D. tech. Sciences V.F. Krotyuk (Institute of Public Buildings).
1 area of use
1.1 This SP is intended for the technological design of swimming pool baths for various purposes: for sports activities and training in swimming, diving, water flooring, synchronized swimming and other sports, for physical culture and recreation activities for the population, for teaching swimming to children and adults, as well as for sports and recreational and rehabilitation activities for disabled people (including disabled children).
1.2 The provisions of this document apply to the design of newly constructed and reconstructed buildings and premises intended for water sports and recreational activities.
1.3 Dimensions and markings of playgrounds and venues for competitions (classes), parameters of safety zones (including above the playing field), established by the rules for holding the relevant types of competitions, should be taken as mandatory technological requirements.
The parameters of sports halls with accompanying groups of necessary premises, given in this Code of Rules, are the functional and technological basis for drawing up a design program for sports buildings and complexes, which should be designed according to the relevant building regulations.
1.4 The provisions of the document are also used in determining the one-time occupancy of the halls and designing auxiliary premises: for changing clothes, storing clothes and personal hygiene for those involved; inventory at the halls, etc., enabling the full functioning of physical culture and sports halls.
1.5 This joint venture does not include: special rooms for disabled people, including children; sports halls of educational institutions (children's preschool institutions and educational institutions); specialized rooms for children sports sections; as well as areas of the halls where seats for spectators are located.
1.6 The provisions of the Code of Rules apply to the design of halls with various pool baths specially provided for placement in them, which can be located both in separate buildings and in sports complexes, and when embedding them in other structures.
2 Normative references
SNiP 23-03-2003 Noise protection
SNiP 23-05-95* Natural and artificial lighting
SNiP 35-01-2001 Accessibility of buildings and structures for people with limited mobility
SNiP 41-01-2003 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning
SNiP 2.03.11-85 Protection building structures against corrosion
SNiP 2.04.01-85* Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings
SNiP 2.04.02-84* Water supply. Outdoor networks and facilities
SNiP 2.08.02-89* Public buildings and structures (as amended No. 1 - 5)
SNiP II-25-80 Wooden structures
SP 35-101-2001 Design of buildings and structures, taking into account accessibility for people with limited mobility. General provisions
SP 35-103-2001 Public buildings and facilities accessible to visitors with limited mobility
SanPiN 2.1.2.1188-03 Swimming pools. Hygienic requirements for the device, operation and water quality. Quality control
SanPiN 2.1.2.1331-03 Hygienic requirements for the design, operation and quality of water in water parks
SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01 Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems. Quality control
SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00 Hygienic requirements for the protection of surface waters
SP 2.1.5.1059-01 Hygienic requirements for the protection of groundwater from pollution
SP 4723-88 Sanitary rules for the design and operation of centralized hot water supply systems
GOST 464-79 Grounding for fixed installations of wire communication, radio relay stations, wire broadcasting radio stations and antennas, systems for collective television reception. Resistance rates
PUE Rules for the installation of electrical installations
NPB 88-2001* Fire extinguishing and signaling installations. Design norms and rules
NPB 104-03 Warning and evacuation control systems in case of fires in buildings and structures
3 General
3.1 According to their purpose, pools are divided into the following types:
splashing - for introducing children to water up to school age;
children's - for teaching swimming to children of younger and middle age;
educational - for teaching swimming to older children and adults, for teaching young and middle-aged children when moving from a nursery to the main bath, as well as for recreational swimming for older people;
swimming pools intended for training athletes and students;
diving pools;
universal training pools equipped for swimming, water flooring, diving and intended for swimming training, recreational activities, training, as well as for local competitions without spectators or in the presence of a limited number of spectators (up to 600 seats in indoor and up to 1200 seats in open facilities);
universal demonstration pools designed for major competitions with more than 600 seats in indoor and 1200 seats in from indoor pools.
3.2 Functionally, the construction of the pool combines one or more baths, rooms and devices for servicing students, spectators (mainly in universal and demonstration pools), as well as rooms with devices that ensure its technical operation.
The internal layout of the main premises of the pool must comply with the hygienic principle of flow: the promotion of visitors is carried out according to the functional scheme - wardrobe, dressing room, shower room, foot bath, pool bath. It is recommended to arrange walk-through cabins for changing clothes with two entrances (exits) in the dressing room, it should also be provided so that the visitor cannot go to the bath without passing the shower.
The functional diagram of the complex pool is shown in Figure 3.1*.
3.3 The provisions of the Code of Rules determine the necessary parameters, the organization of functional areas and the equipment of the pool premises in buildings for sports and recreation and rehabilitation classes, taking into account the provision of the necessary accessibility requirements for people with disabilities of various ages.
Designed premises, buildings and structures of swimming pools can be adapted in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 35-01, SP 35-101 and SP 35-103 for use by people with disabilities of various ages (disabled) with a corresponding entry in the design assignment.
3.4 The choice of a land plot for the location of the pool must be agreed with the bodies of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of Russia.
3.5 Designed swimming pools must comply with the norms, standards and requirements for fire safety of buildings and structures approved in the prescribed manner.
3.6 When arranging outdoor pools, the area of the allotted area is planted with at least 35% shrubs or stunted trees. Along the perimeter of the site, wind and dust protection strips of tree and shrub plantations are provided and at least 20 m - from the side of main roads with heavy traffic.
The distance of the outdoor pool baths from the red line must be at least 15 m; from the territory of hospitals, children's school and preschool institutions, as well as residential buildings and parking lots - at least 100 m.
3.7 Water parks (pools or a complex of pools that include water attractions: slides, artificial waves, currents, waterfalls, fountains, hydro and air massage devices, etc., recreation areas and other functional facilities) should be located in a separate area in residential, park or recreational area.
3.8 Placement of car parks at the water park for visitors is regulated by the requirements of sanitary rules for sanitary protection zones and sanitary classification of enterprises, structures and other objects.
3.9 Baths for recreational swimming, bathing, general developmental exercises and games in the water, as well as for teaching non-swimmers, with auxiliary facilities for their maintenance, can be designed in separate buildings, be part of sports pool buildings, and also be attached or built-in in public buildings in accordance with applicable building codes and regulations.
4 Parameters and equipment of pool baths
4.1 Sports baths
Bathtubs for swimming
4.1.1 For sports swimming, as well as for alternate use by various types sports, specialized and universal baths of the following sizes and throughputs indicated in Table 4.1 should be used.
Schemes of longitudinal profiles of bathtubs (for sports swimming and universal) are shown in Figure 4.1.
4.1.2 The height of the bath halls for sports swimming (from the surface of the bypass path to the bottom of the protruding structures) without jumping devices and places for spectators is taken at least 6 m with a bath length of 50 and 33.33 m; with a bath length of 25 m - 5.4 m.
4.1.3 The width of the track for sports swimming is assumed to be 2.5 m. Behind the outer tracks to the walls of the bath, free strips of water are provided with a width of 0.5 m, or 2.5 m in cases of Olympic Games or world championships.
For the Olympic Games, 8 lanes are provided, as well as 50 m long baths, and 25 m long for the World Swimming Championships. The baths are provided with touch panels of automatically operating equipment on the starting end wall and on the turning end. The distance between the axes of adjacent lanes must be at least 2.5 m. If the baths for sports swimming and for jumping are located in the same room, then the minimum distance between them must be 5.0 m.
The system of regulatory documents in construction
CODE OF RULES FOR DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
SWIMMING POOLS
SP 31-113-2004
Moscow
2005
Foreword
1 DEVELOPED by the St. Petersburg State Academy of Physical Culture. P.F. Lesgaft (SPb. GAFC) of Rossport and the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Scientific and Design Institute of Educational, Commercial and Leisure Buildings" (Institute of Public Buildings) as part of the implementation of paragraph 17 of the activities of the subprogram "Physical education and rehabilitation of children, adolescents and youth in the Russian Federation (2002 - 2005)" of the federal target program "Youth of Russia (2001 - 2005)"
2 INTRODUCED by the St. Petersburg State Academy of Physical Culture. P.F. Lesgaft
3 REPRESENTED by the Department of Architecture and the Department of Standardization, Technical Regulation and Certification of the Gosstroy of Russia
4 APPROVED by orders of the rector of the St. Petersburg State Academy of Physical Culture. P.F. Lesgaft dated February 9, 2005 No. 25 and director of the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Institute of Public Buildings" dated April 23, 2004 No. 11
5 APPROVED AND RECOMMENDED for use as a regulatory document in construction by the letter of the Gosstroy of Russia on April 30, 2004 No. LB-322/9 and the Federal Agency for Physical Culture, Sports and Tourism by Order No. 24 of February 26, 2005
6 INTRODUCED FOR THE FIRST TIME
Introduction
The development of the system of sports and health facilities in our country is becoming increasingly important. At the same time, there is a need to ensure the availability of recreational and sports activities for all age groups of the population, both healthy people and the disabled.
The regulatory document was developed in accordance with the State Contract with Rossport No. 209 dated December 10, 2002 as part of the subprogram "Physical education and rehabilitation of children, adolescents and youth in the Russian Federation (2002 - 2005)", clause 17 "Development of architectural and planning standards for their application in the construction of sports and recreation and sports facilities, taking into account the possibility of their use by disabled children.
The set of rules is developed in the development of SNiP 2.08.02-89 * "Public buildings and structures" and is a document of the federal level. It deals with the functional and technological requirements for the design of pool baths for sports and leisure activities, available for sports and recreational activities. The document was developed taking into account the requirements for baths and pool rooms, reflected in the rules of the competition, based on the design experience and practice of operating pools for various purposes.
When developing this Code of Rules, the following conditions for organizing the spatial environment in buildings and premises were taken into account:
dimensions of a person and groups of people in various positions, taking into account the characteristics of different age groups of healthy people and disabled people;
functional and technological (sports) processes associated with individual physiological and social functions of a person, as well as with the operation of simulators, equipment and the use of inventory;
requirements for acoustics, soundproofing of halls;
norms of natural and artificial illumination of premises, frequency of air exchange, etc.;
quality and frequency of water exchange in pool baths;
The following materials are partially used in the text and graphic part of the Code of Rules:
· Pool Design (Reference Guide to SNiP 2.08.02-89). - M.: Stroyizdat, 1991.
· Normals of planning elements of residential and public buildings:
Issue NP 5.3.2-76 Auxiliary premises of sports facilities. - M.: Stroyizdat, 1976.
Scientific editor - Ph.D. archit.A. M. Garnets.
Computer graphics - archit. TO.IN. Karpacz(TsNIIEP housing), Ph.D. tech. Sciences IN.F. Crotyu To(Institute of Public Buildings).
SP 31-113-2004
CODE OF RULES ON DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
SWIMMING POOLS
swimming pools
1 area of use
1.1 This SP is intended for the technological design of pool baths for various purposes: for sports activities and training in swimming, diving, water flooring, synchronized swimming and other sports, for physical culture and recreation activities for the population, for teaching swimming to children and adults, as well as for sports and recreational and rehabilitation activities for disabled people (including disabled children).
1.2 The provisions of this document apply to the design of newly constructed and reconstructed buildings and premises intended for water sports and recreational activities.
1.3 Dimensions and markings of playgrounds and venues for competitions (classes), parameters of safety zones (including above the playing field), established by the rules for holding the relevant types of competitions, should be taken as mandatory technological requirements.
The parameters of sports halls with accompanying groups of necessary premises, given in this Code of Rules, are the functional and technological basis for drawing up a design program for sports buildings and complexes, which should be designed according to the relevant building regulations.
1.4 The provisions of the document are also used in determining the one-time occupancy of the halls and designing auxiliary premises: for changing clothes, storing clothes and personal hygiene for those involved; inventory at the halls, etc., enabling the full functioning of physical culture and sports halls.
1.5 This joint venture does not include: special rooms for disabled people, including children; physical culture halls of educational institutions (children's preschool institutions and educational institutions); specialized halls for children's sports sections; as well as areas of the halls where seats for spectators are located.
1.6 The provisions of the Code of Practice apply to the design of halls with various pools specially designed for placement in them, which can be located both in separate buildings and in sports complexes, and when they are built into other structures.
1.7 The set of rules contains advisory provisions, norms and rules. The provisions of this document become mandatory for all participants in the design and construction process when they are included in the approved design assignment.
2 Normative references
* Figures referenced in the text are given in the appendix.
3.3 The provisions of the Code of Rules determine the necessary parameters, the organization of functional areas and the equipment of the pool premises in buildings for sports and recreation and rehabilitation classes, taking into account the provision of the requirements for the necessary accessibility for people with disabilities. handicapped different ages.
Designed premises, buildings and structures of swimming pools can be adapted in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 35-01, SP 35-101 and SP 35-103 for use by people with disabilities of various ages (disabled) with a corresponding entry in the design assignment.
3.4 The choice of a land plot for the location of the pool must be agreed with the bodies of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of Russia.
3.5 Designed swimming pools must comply with the norms, standards and requirements for fire safety of buildings and structures approved in the prescribed manner.
3.6 When arranging outdoor pools, the area of the allotted area is planted with at least 35% shrubs or stunted trees. Along the perimeter of the site, wind and dust protection strips of tree and shrub plantations are provided and at least 20 m - from the side of main roads with heavy traffic.
The distance of the outdoor pool baths from the red line must be at least15 m; from the territory of hospitals, children's school and preschool institutions, as well as residential buildings and parking lots - at least 100 m.
3.7 Water parks (pools or a complex of pools that include water attractions: slides, artificial waves, currents, waterfalls, fountains, hydro and air massage devices, etc., recreation areas and other functional facilities) should be located in a separate area in residential, park or recreational area.
3.8 Placement of car parks at the water park for visitors is regulated by the requirements of sanitary rules for sanitary protection zones and sanitary classification of enterprises, structures and other objects.
3.9 Baths for recreational swimming, bathing, general developmental exercises and games in the water, as well as for teaching non-swimmers, with auxiliary facilities for their maintenance, can be designed in separate buildings, be part of buildings sports pools, as well as be attached to or built into public buildings in accordance with applicable building codes and regulations.
4 Parameters and equipment of pool baths
4.1 Sports baths
BathsFor swimming
4.1.1 For sports swimming, as well as for alternate use in various sports, specialized and universal baths of the following sizes and throughputs indicated in the table should be used.
Schemes of longitudinal profiles of bathtubs (for sports swimming and universal) are shown in the figure.
4.1.2 The height of the bath halls for sports swimming (from the surface of the bypass path to the bottom of the protruding structures) without jumping devices and places for spectators is taken at least 6 m with a bath length of 50 and 33.33 m; with a bath length of 25 m - 5.4 m.
4. 1.4 The capacity of one track is taken as the basis for calculating the capacity of the pool. Therefore, for tracks 25 meters long, it is accepted 8 people, and for 50 meters 12 people. When organizing classes across the bath or on paths of reduced width for a bath of 50 × 25 m, the calculation should be carried out for 20 transverse paths with a total capacity of 160 people, and for a bath of 50 × 21 m - for 10 longitudinal paths with a width of 2 m, i.e. . for 120 swimmers.
Bath 25× 16 m can be divided into eight lanes 2 m wide with a total capacity of 64 people; in a 25x11 m bath there can be 6 lanes of 1.8 m each (capacity 48 people), and a 25x8.5 m bath can accommodate 40 swimmers on 5 lanes.
The capacity of educational children's baths that are not divided into lanes is calculated on the basis of a lesson methodology that provides for a group of 20 people.
The capacity when playing water polo on a "full-length" court 30 × 20 m - 25, and in 25-meter baths - 15 people.
Each platform of the tower and each springboard can have 6 jumpers at the same time, but the capacitya complete set of jumping devices (towers with platforms 10; 7.5; 5; 3 m, two springboards each 3 and 1 m high), taking into account the difference in time of jumps, is accepted in 30 people.
4. 1.5 Direction indicators should be mounted on fixed posts located 5 m from each end wall. Ropes with flags are hung across the pool at a height of 1.8 to 2.5 m from the surface of the water. At a distance of 15 m from each end wall, clear marks are made on both side walls of the pool and, if possible, on each lane separator (figure ).
4. 1.6 The false start rope must be suspended across the pool at a height of at least 1.2 m above the water level on racks fixed 15 m from the start. The rope must be attached to the uprights using a quick release mechanism. When dropped, the rope must cover all lanes.
4.1.7 The lane axes shall be marked in a dark contrasting color and applied to the bottom of the pool in the center of each lane: width 0.2 - 0.3 m, length 46.0 m for 50-meter pools; 21.0 m in 25 m pools.
Each marking line must end 2 m before the end wall with a clear transverse line 1 m long and the same width as the longitudinal line. Axes marking lines are also applied to the end walls, targets of the same width as along the tracks. They should go from the curb to the bottom of the pool. A transverse line 0.5 m long is drawn at a depth of 0.3 m from the surface of the water, counting from the center of the transverse lines.
4.1.8 When a floating bulkhead is used as the end wall, it should extend the full width of the tub and provide a hard, smooth, non-slip, stable vertical surface. Touch panels can be installed on it no deeper than 0.8 m below the water level and no higher than 0.3 m above the water level. Neither above nor below the water level should there be any unforeseen openings into which the swimmer's hands, feet or fingers or toes could get caught. The design of the bulkhead should be such that it can move freely without causing any currents or turbulence in the water.
Equipment baths For swimming
4.1.9 Overflow gutters (foam troughs) are used to maintain a constant water level, remove the contaminated top layer, and also to dampen waves that occur during swimming. Schemes of profiles of the longitudinal walls of the baths are shown in the figure.
There are two types of overflow gutters: with a board in the plane of the water and a bypass path and with boards rising above the water. In the first type, water, overflowing through a roller - a handrail 5 - 6 cm high, enters the bypass path, where it is discharged into a lattice ladder installed at a distance of 30 - 35 cm from the edge of the bath. In the second option, the water flow is provided in the longitudinal profile of the gutter bottom, having a slope of 0.01 - 0.2 to the ladders, which are installed every 3 - 5 m.
Gutters of the first type are made around the entire perimeter of the bath, while stationary or removable screens are installed at the ends to repel when turning and register the finish. The first type dampens waves better, is simpler and more economical, as it reduces the height of the walls of the bath by 30 - 35 cm and, by combining the structures of the side and the bypass path, makes it possible to reduce the total span of the hall by the thickness of the sides (by about 1 m), which is very significant in small mass pools.
Overflow gutters of the second type are more hygienic, since contaminated water does not enter the bypass path. However, they exclude the possibility of installing hooks for floats and a standard handrail and are therefore installed only along the longitudinal sides of the bath.
4.1.10 In indoor baths with a length of 50 and 25 m, intended mainly for sports swimming, it is recommended to design the longitudinal walls of the bath according to option "a" of the figure. In open year-round baths, the profile of the bath walls according to option “a” is usually not accepted.
The grate of the overflow gutter in options "a" and "b" is arranged flush with the surface of the bypass path.
The upper plane of the wall in option "d" and the treads of the steps to get out of the water in option "b" are non-slip.
The edge of the side of the wall with option "a", the edge of the overflow chute with options "d" and "e", as well as the edges of the steps for exiting the water with option "b" are rounded.
In baths for teaching non-swimmers, it is recommended to design the wall according to option “d”, but option “d” can also be used, in this case the wall thickness on top can be reduced from 0.5 to 0.25 m.
4.1. 11 On both longitudinal walls of baths for sports swimming, as well as universal baths, a ledge for rest of 0.1 - 0.15 m should be provided. A ledge for rest is arranged in places where the water depth is more than 1.2 m.
In specialized baths for jumping into the water, along the wall along which the jumping devices are located, gentle steps are arranged to exit the water, and a ledge for resting under them is not provided (fig. b ).
4.1.12 In bathtubs for sports swimming, one or both end walls (with a water depth at the wall of at least 1.8 m) should be provided with starting tables 0.50 - 0.75 m high above the water level.
Each starting table is numbered on four sides with Arabic numerals, which must be clearly visible. Lane number 1 is located on the right side if you stand at the start facing the pool tub, with the exception of 50-meter swims, in which you can start from the opposite end. Touchpads can be numbered from the top.
Starting tables are located along the axis of each track for sports swimming. Concrete bedside tables are faced with glazed tiles. In the demonstration pools, inventory all-metal cabinets with an electronic device for fixing the start and the time of passing the distance are used. Schemes of starting tables with handrails and end walls of bathtubs are shown in the figure.
In baths for training sessions, instead of starting tables, it is allowed to provide a starting bridge along the entire length of the end wall. The working surface of the bedside table (bridge) is non-slip. For bedside tables with a height of 0.55 m or more from the surface of the bypass path, a step is provided.
To start swimming on the back under the bedside table in the plane of the bathtub wall, metal handles - handrails are installed. Handrails are horizontal, vertical, combined and are installed 0.4 - 0.6 m above the water. Cross-sectional diameter of the handrails for the start in swimming on the back - 0.0 3 - 0.04 m.
In cases where the longitudinal walls are made according to option "a", the profile of the end wall is provided according to option I(see figure). In cases where the longitudinal walls are made according to option "d" (see figure), the end wall is provided according to option II or III (see figure). A ledge for rest along the end walls of the baths is not provided. The end walls of bathtubs for sports swimming in the surface part to a height of at least 0.3 m and in the underwater part to a depth of at least 0.8 m are non-slip.
Robust and rigid screen (fixed or removable) included with option I , is installed along the entire length of the wall, flush with it and has a non-slip surface (facing the bath).
4.1.13 The placement of embedded devices and the marking of the bath for sports swimming are shown in the figure. For recreational swimming, additional niches with hooks for attaching floats for marking tracks in the bath can be provided:
50 × 25 m - for tracks 2.5 m wide, located along the transverse axis of the bath;
50 × 21 m - for 10 tracks 2 m wide;
25 × 16 m - for 8 tracks 1.9 m wide;
25× 11 m - for 6 tracks 1.75 m wide;
25 × 8.5 m - for 5 tracks 1.6 m wide each.
Embedded devices should not protrude from the plane of the walls of the bath and the bypass path. The stripes marking the axes of the tracks stand out in contrast against the background of the walls and bottom; deviation from the dimensions shown in the figure can be within +0.05 m.
With longitudinal walls that do not protrude above the water level (figure , option "a"), nests under the rack for restart cords and with signal flags are installed on the bypass path behind the overflow chute.
For hanging floats separating the surface of the water in the walls of the bath, niches of 15 × 15 cm in size with hooks or rings are installed. If classes are held across the baths (for example, in a 50 × 25 m bath) or on paths of reduced width, additional niches and embedded devices for hanging floats should be provided.
4. 1.14 In all baths, stairs should be provided for entering and exiting the water. In baths for sports swimming 50 m long, three, 25 and 33.33 m long, two ladders should be provided on each longitudinal side, placing them in niches that do not protrude from the plane of the walls of the baths.
In bathtubs for jumping into the water, one ladder or step is allowed across the entire width (p.).
The scheme of the ladder for getting out of the water in the baths for sports swimming and water polo is shown in the figure. Niches for stairs measuring 0.8 - 1 × 0.2 - 0.25 m in plan should only reach the ledge for relaxation, and with a water depth of more than 70 cm - below the ledge, reach the bottom for use when cleaning and repairing the bath. The lower part of the ladder from the ledge to the bottom may not be recessed into a niche or be removable. The handrails of the stairs are made of different heights for convenient use of visitors different ages. Step ladders must be reliably protected from corrosion and are usually made of stainless steel pipes with a diameter of 40 mm. The width of the stairs is 0.6 m, the distance between the steps is 0.3 m. The stairs are located no closer than 3 and no further than 5 m from the end walls; in the case of the installation of viewing windows or overflows, they are located further from the end wall than the viewing window or overflow.
4.1. 15 The height of the halls with baths for diving, as well as the halls with universal baths (within the jump part) should be taken according to the drawing. The height of the halls of the demonstration pools is also determined by the height of the podium.
jumpingV water
4.1.16 The dimensions of the baths for jumping into the water and the arrangement of devices for jumping should be taken in accordance with the given composition of the devices, guided by the parameters and dimensions given in the figures and in the table.
Before sending an electronic application to the Ministry of Construction of Russia, please read the rules of operation of this interactive service set out below.
1. Electronic applications in the field of competence of the Ministry of Construction of Russia filled in in accordance with the attached form are accepted for consideration.
2. An electronic appeal may contain a statement, complaint, proposal or request.
3. Electronic appeals sent through the official Internet portal of the Ministry of Construction of Russia are submitted for consideration to the department for working with citizens' appeals. The Ministry provides an objective, comprehensive and timely consideration of applications. Consideration of electronic appeals is free of charge.
4. In accordance with the Federal Law of May 2, 2006 N 59-FZ "On the procedure for considering applications from citizens of the Russian Federation", electronic applications are registered within three days and sent, depending on the content, to the structural divisions of the Ministry. The appeal is considered within 30 days from the date of registration. An electronic appeal containing issues, the solution of which is not within the competence of the Ministry of Construction of Russia, is sent within seven days from the date of registration to the appropriate body or the appropriate official, whose competence includes resolving the issues raised in the appeal, with notification of this to the citizen who sent the appeal.
5. An electronic appeal is not considered when:
- the absence of the name and surname of the applicant;
- indication of an incomplete or inaccurate postal address;
- the presence of obscene or offensive expressions in the text;
- the presence in the text of a threat to the life, health and property of an official, as well as members of his family;
- using a non-Cyrillic keyboard layout or only capital letters when typing;
- the absence of punctuation marks in the text, the presence of incomprehensible abbreviations;
- the presence in the text of a question to which the applicant has already received a written answer on the merits in connection with previously sent appeals.
6. The response to the applicant of the appeal is sent to the postal address specified when filling out the form.
7. When considering an appeal, it is not allowed to disclose the information contained in the appeal, as well as information relating to the private life of a citizen, without his consent. Information about the personal data of applicants is stored and processed in compliance with the requirements of Russian legislation on personal data.
8. Appeals received through the site are summarized and submitted to the leadership of the Ministry for information. The answers to the most frequently asked questions are periodically published in the sections "for residents" and "for specialists"
Approved Order of the Ministry of Construction and Housing and Communal Services of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2017 N 1716 / pr
Code of Practice SP-310.1325800.2017
"POOLS FOR SWIMMING. DESIGN RULES"
swimming pools. design rules
Introduced for the first time
Introduction
This set of rules has been developed taking into account the increased requirements for the conditions for teaching swimming to children of preschool and school age, recreational activities among the population, and also taking into account changes in the rules and regulations of competitions in water sports, requirements for the parameters and equipment of swimming pools intended for sports events.
The set of rules ensures compliance with the requirements of the Federal Laws of December 30, 2009 N 384-FZ "Technical Regulations on the Safety of Buildings and Structures", of November 22, 2009 N 261-FZ "On Energy Saving, Increasing Energy Efficiency and on Amending Certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation", dated July 22, 2008 N 123-FZ "Technical regulations on fire safety requirements".
The set of rules was developed by the group of authors: Institute of Public Buildings LLC (head of the work - Candidate of Architecture D.A. Rozhdestvensky, responsible executors - Candidate of Architecture A.M. Garnets, senior researcher L.V. Sigacheva); OFSOO "Russian Association of Sports Facilities" (Doctor of Psychology, V.B. Myakonkov); OOO "Institute of Sports Facilities" (A.V. Trukhan).
1 area of use
1.1 This set of rules establishes the requirements for the design of swimming pools intended for accustoming preschool children to water, teaching swimming, training sessions for schoolchildren, physical culture and recreation classes for citizens, for sports events.
1.2 This set of rules applies to the design of newly built and reconstructed buildings, structures and premises of swimming pools, regardless of their form of ownership.
2 Normative references
This set of rules uses normative references to the following documents:
GOST R 53491.1-2009 Pools. Water preparation. Part 1. General requirements
GOST R 53491.2-2012 Pools. Water preparation. Part 2. Security Requirements
SP 1.13130.2009 Fire evacuation systems. Evacuation routes and exits (with change No. 1)
SP 3.13130.2009 Fire protection systems. Fire warning and evacuation control system. fire safety requirements
SP 5.13130.2009 Fire protection systems. Fire alarm and fire extinguishing installations are automatic. Design norms and rules (with change No. 1)
SP 28.13330.2017 "SNiP 2.03.11-85 Corrosion protection of building structures"
SP 30.13330.2016 "SNiP 2.04.01-85* Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings"
SP 42.13330.2016 "SNiP 2.07.01-89* Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements"
SP 51.13330.2011 "SNiP 23-03-2003 Noise protection" (with amendment No. 1)
SP 52.13330.2016 "SNiP 23-05-95* Natural and artificial lighting"
SP 59.13330.2016 "SNiP 35-01-2001 Accessibility of buildings and structures for people with limited mobility"
SP 60.13330.2016 "SNiP 41-01-2003 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning"
SP 64.13330.2017 "SNiP II-25-80 Wooden structures"
SP 113.13330.2016 "SNiP 21-02-99* Car parking"
SP 118.13330.2012 "SNiP 31-06-2009 * Public buildings and structures" (with amendments No. 1, No. 2)
SP 132.13330.2011 Ensuring anti-terrorist protection of buildings and structures. General design requirements
SP 133.13330.2012 Wired radio broadcasting networks in buildings and structures (with change No. 1)
SP 136.13330.2012 Buildings and structures. General provisions for designing taking into account accessibility for people with limited mobility (with change No. 1)
SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01 Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems. Quality control. Hygienic requirements for ensuring the safety of hot water supply systems
SanPiN 2.2.1 / 2.1.1.1076-01 Hygienic requirements for insolation and sun protection of residential and public buildings and territories
SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03 Hygienic requirements for natural, artificial and combined lighting of residential and public buildings
SanPiN 2.1.2.1188-03 Swimming pools. Hygienic requirements for the device, operation and water quality. Quality control
Note - When using this set of rules, it is advisable to check the validity of reference documents in the public information system - on the official website of the federal executive body in the field of standardization on the Internet or according to the annual information index "National Standards", which was published as of January 1 of the current year , and according to the issues of the monthly information index "National Standards" for the current year. If an undated referenced document has been replaced, it is recommended that the current version of that document be used, taking into account any changes made to that version. If the referenced document is replaced by a dated reference, it is recommended that the version of this document with the year of approval (acceptance) indicated above be used. If, after the approval of this set of rules, a change is made to the referenced document to which a dated reference is given, affecting the provision to which the reference is given, then this provision is recommended to be applied without taking into account this change. If the reference document is canceled without replacement, then the provision in which the link to it is given is recommended to be applied in the part that does not affect this link. It is advisable to check the information on the operation of the sets of rules in the Federal Information Fund of Standards.
3 Terms and definitions
In this set of rules, the following terms are used with their respective definitions:
3.1 VVIP zone: A completely autonomous territory (space) with limited access, separate maintenance and an exclusive set of services, a dedicated seating area in the most comfortable part of the tribune, providing best review sports event, designed for special guests, with seats and additional rooms of increased comfort and security.
3.2 VIP zone: Dedicated zone for spectators and additional rooms of increased comfort and security with an additional set of services.
3.3 all-Russian register of sports facilities: a register formed in order to systematize data on the number, purpose and condition of sports facilities located on the territory of the Russian Federation and used for holding sports events and sports events included in the Unified calendar plan for interregional, all-Russian and international sports events and sports events, calendar plans for physical culture events and sporting events of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
3.4 support zone: A set of premises that provide a sports facility with related maintenance and services functions for various client groups during sports events.
3.5 spectator area: The space in the immediate vicinity of the competition area intended for spectators of sports events held at the sports facility.
3.6 organizers area: A set of premises intended for the accommodation and work of the organizers of a sporting event.
3.7 sports zone (sports zone): Main space (territory) sports facility, where the sporting event is directly held, including a security zone that separates the sports area from spectators or structural elements, a technical area with accommodation for participants and judges, as well as equipment necessary for holding a sporting event.
3.8 category of a sports facility: Compliance of a sports facility with the requirements of the level of sports events held (A - international and all-Russian sports events; B - interregional sports events; C - other sports events).
3.9 client groups: Divided into categories (segments) guests, organizers, participants, spectators, judges, service and technical personnel, as well as other groups located at the sports facility during the sports event.
3.10 sports facility: A building, structure or complex intended for physical culture and/or sports events.
3.11 official sports events and sports events: Sports events and sports events included in the Unified calendar plan for interregional, all-Russian and international sports events and sports events, calendar plans for sports events and sports events of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipalities.
3.12 video display system: Scoreboard, cube, other devices that display video information about a sporting event.
3.13 timing system: A set of electronic equipment that provides accurate timekeeping and fixing the results of competitors.
3.14 sports equipment: Devices, fixtures, shells, the placement of which on a sports facility is provided for by the rules of competitions in sports.
3.15 sports facility: An engineering and construction facility created for holding sports events and (or) sports events and having spatial and territorial boundaries.
3.16 sports competition: A competition (match) among athletes or teams of athletes in various sports (sports disciplines) to identify the best participant in the competition (match), held according to the regulations (regulations) approved by its organizer.
3.17 sports events: Sports competitions, as well as training events, including theoretical and organizational parts, and other events in preparation for sports competitions with the participation of athletes.
3.18 physical culture events: Organized physical culture classes for citizens.
3.19 functional area: Premises (space), within the boundaries of a sports facility, with an established functional purpose and mode of use.
4 General provisions
4.1 Swimming pools according to their functional purpose are divided according to the classification shown in Figure 4.1.
4.2 Swimming pools for preschool children are intended for use by preschool educational organizations, children's medical institutions, sanatoriums, camps, etc.
Training pools - for use by general educational organizations in physical education classes, children's sanatoriums, camps, in places of mass recreation for children and adults.
Health pools - for placement and use in places of residence and mass recreation of citizens, as part of health centers of enterprises, in military units, fitness clubs, sanatoriums, rest homes, etc.
4.3 Swimming pools for preschool children and training pools are recommended to be placed in the buildings of preschool educational and general educational organizations or extensions to them. At the same time, the pools can be used by nearby children's educational organizations, which should be taken into account by their planning structure.
4.5 Sports pools are designed for sports events, competitions of various levels, training events in preparation for sports competitions.
4.6 Swimming pools, subject to SanPiN 2.1.2.1188, can be designed open and closed.
4.7 The total (usable and estimated) area, building volume, built-up area and number of storeys of swimming pools should be determined according to SP 118.13330.
4.8 Buildings, structures and premises of swimming pools should be designed taking into account accessibility for people with limited mobility in accordance with SP 59.13330 and SP 136.13330.
4.9 Ensuring integrated security and anti-terrorist protection of pools should be designed in accordance with SP 132.13330.
4.10 The area of plots of detached buildings of sports pools is determined according to SP 42.13330.
4.11 The area and number of parking spaces in the pool areas are determined according to SP 42.13330 and SP 113.13330.
4.12 The width of the traffic routes along the territory of the basins is determined by SP 59.13330.
4.14 It is recommended to plant shrubs and coniferous trees along the perimeter of open pool areas on strips of at least 5 m wide.
5 Parameters and equipment of pool baths
Sports and recreational pools
5.1 For fitness and recreation pools, baths should be used, the dimensions and surface area of which are given in Appendix A.
5.2 In pool baths, a bottom slope should be provided to ensure that people of different heights can choose the appropriate depth. Recommended slope (depth) values are given in Appendix A.
5.3 In the baths of the pools, it is also necessary to provide for a technological slope of the bottom, intended for draining water, directed to the places of its release (funnel). The slope value should be taken within 1% - 4%. The drain slope is normally directed perpendicular to the slope of 5.2.
5.4 The height of the premises for placing pools with a length of 10 m or more, measured from the surface of the bypass path around the pool to the bottom of the protruding structures, should be taken at least 6 m.
5.5 In the baths of pools 16 and 25 m long, it is necessary to provide for the division of the water surface into paths. The width of the path should be taken equal to 2 m. Behind the extreme paths to the walls of the bath, free strips of water 0.5 m wide are provided.
5.6 The maximum number of people simultaneously in the pool bath should be determined based on the values of the estimated water surface area given in Appendix A.

5.8 It is recommended to design the boards and grate of health-improving pools as for sports pools (Figure 5.2).


5.9 The grate of the overflow gutter should be designed flush with the surface of the bypass (see 5.21).
5.10 The edge of the side of the pool should be designed rounded.
5.11 Along both longitudinal walls of bathtubs, the depth of which exceeds 1.2 m, a ledge is provided for swimmers to rest (see 5.48).
5.12 Starting bollards for competitions (Figure 5.3) are provided for pools 16 and 25 m long. The bollards should be located on the side of the pool 1.8 m deep.


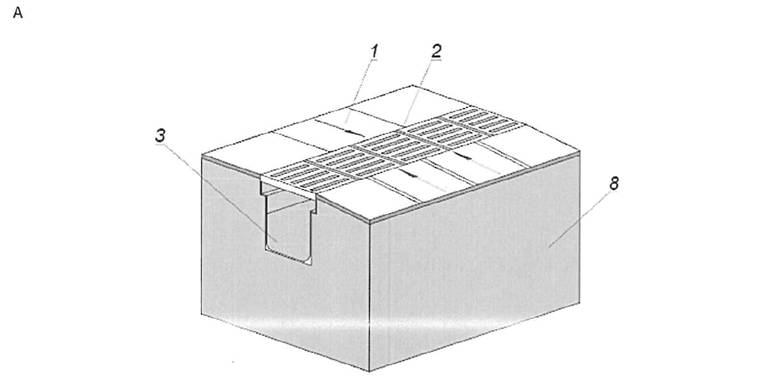



5.13 For fastening the floats for marking the tracks in the end walls of the baths, niches are provided for placing embedded devices for fastening the floats in them. Embedded devices should not protrude from the plane of the bath walls.
5.14 For the arrangement of tracks in the transverse direction in swimming pools, embedded devices can also be provided in the longitudinal walls of the pool.
5.15 In pool baths, ladders should be provided for exiting the water. In the baths of pools 16 and 25 m long, there are 2 ladders located on each longitudinal side. Stairs should be placed in niches, deepening them in relation to the plane of the walls of the baths. The diagram of the staircase for entry / exit from the water is shown in Figure 5.4. The handrails of the stairs are made of different heights for convenient use by visitors of different heights. Ladders are located no closer than 3 and no further than 5 m from the end walls of the pool. Flat stairs should be considered preferable.

5.16 Water renewal systems that provide for the removal of water through holes in the walls or bottom of the pool are not used for sports and recreation pools.
5.17 The distance between pool baths located in the same room should be at least 5 m.
5.18 On the floor area, along the perimeter of the pool baths, for exercise and recreation of swimmers, accommodation of coaches and judges, personnel, bypass paths are provided.
5.19 The width of the walkways around the pools without starting tables is taken at least 1.5 m from the water at the indoor pool baths and at least 2 m at the open baths.
5.20 The width of the walkway running along the starting blocks is assumed to be at least 3 m.
5.21 The surface of the walkway must be non-slip with a slope towards the overflow chute - 1% - 2%.
5.22 In outdoor pools, it is recommended to design a bypass path with heating.
5.23 Conditions of accessibility for people with limited mobility (MGN), educational and recreational pools are provided, for children of preschool age, the adoption of special measures for the accessibility of pools is not required.
5.24 Swimming pools accessible to MGN are recommended to be provided as part of specialized sports and recreation complexes for the disabled and Paralympic athletes. Planning solutions and technical devices that ensure the accessibility of pools can be provided for when designing mass recreational pools.
5.25 The depth of specialized recreational pools for MGN should be no more than 1.2-1.4 m.
5.26 Bypass paths of pool baths accessible to MGN, as a rule, should be expanded compared to standard sizes, taking into account their equipping with a tactile strip (for the blind and visually impaired) and additional auxiliary equipment.
5.27 A fence 1 m high is installed along the edge of the bath used by the MGN. In training baths for children with disabilities, a fence 0.65 m high is arranged on three sides.
5.28 Warning color marking is applied to the floor at the edge of the pool bath at the entry/exit points.
5.29 In the shallow part of the bath, a sloping staircase leading into the water with risers at least 0.14 m high and treads at least 0.3 m high is installed.
5.30 Instead of foot walk-through baths, at the exit from the dressing rooms to the pool hall (see 6.12), it is recommended to use mats impregnated with antiseptics for MGN.
5.31 Along the outer boundary of the bypass path of the pool baths for MGN, stationary benches with a height of 0.5 m should be provided. Places for storing wheelchairs should be provided on the bypass path.
Along the walls of the pool along the perimeter of the bypass path, it is recommended to arrange a solid handrail at a height of 0.9 m from the floor. Figure 5.5 shows the layout of the pool hall used by people with limited mobility. Figure 5.6 shows a diagram of the arrangement of tactile strips on the bypass path of the baths.


5.32. Disabled people in wheelchairs can use ordinary fitness pools, provided that special devices are used for lowering / raising disabled people into the pool bath.
5.33 Recommendations for the installation of baths for MGN indoor pools are applicable to outdoor pools. If one-way turnstiles are arranged for the exit of citizens from outdoor pools, then an appropriate exit should be provided for the disabled.
Sports pools
5.34 For sports pools used for one or more sports, specialized and universal baths should be used with the dimensions and throughput given in Appendix B.
For training sessions, it is allowed to use sports baths of other sizes, provided that these requirements are indicated in the design assignment.
Parameters of competition, training and auxiliary zones established by the rules (regulations) sports federations for water sports are mandatory as technological requirements for the design of sports facilities.
The classification of sports pools, depending on the functional purpose of the baths, is shown in Figure 4.1.
Sports swimming pools
5.35 The dimensions of the halls of the baths of sports pools depend on the length of the minimum segment of the distance (path) - 25 m and 50 m and the number of lanes for a simultaneous start - up to 10 (depending on the level of competition and the requirements of the federation for the sport). The width of the walkway in the pool hall for sports swimming should be at least 2 m along the long side of the pool and at least 3 m at the end.
The calculation of the width is taken from the enclosing structure to the edge of the embedded elements (overflow gutter, fastening of the pedestals, etc.) clean.
The parameters of baths for sports swimming are shown in Figures 5.7, 5.8, 5.9.



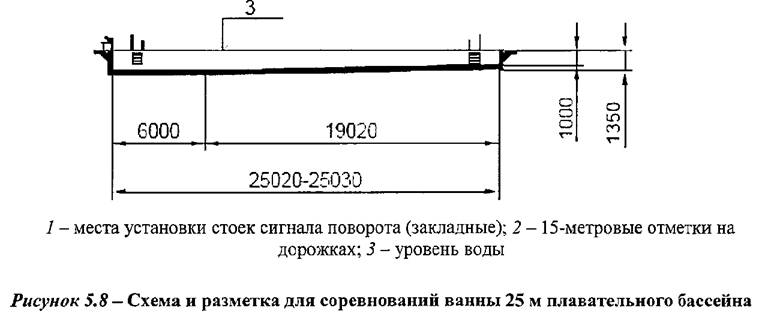

5.36 The width of the track for sports swimming (Figure 5.7) is assumed to be 2500.00 mm (between the axes of the dividing track), for pools of the training level, the width may be reduced to 1800.00 mm. Edge tracks, to create equal conditions in the swim, should be with a wave damping track along the edge of the bath at a distance of 0.3 m from the wall.
5.37 The height of the bath halls for sports swimming (from the surface of the bypass path to the bottom of the protruding structures) without seats for spectators is taken with a bath length of 50 m - at least 6 m; with a bath length of 25 m - not 5.36 less than 5.4 m.
The height of the halls with baths for diving, as well as the halls with universal baths (within the jump part) should be taken according to Figure 5.12.
5.38 For competitions in category A pools, bathtubs 50 m long for 8-10 lanes or 25 m long for 8 lanes must be equipped with contact panels for automatic recording of results, which should be taken into account when designing the length of the bath - it should be increased in accordance with the thickness of the contact panels. The distance between the panels installed on the end walls must be at least 50 m or 25 m.
5.39 When designing a bath for sports swimming and a bath for diving in the same hall, the distance between them must be at least 8 m (preferably 10 m).
5.40 The capacity of a swimming pool should be based on the capacity of one lane. For tracks 25 m long - 8 people, 50 m - 12 people. When organizing sports swimming lessons across the bathtub in a universal bathtub with dimensions of 50x25 m, together with conducting classes in other types water sports, the total calculation should be performed based on the throughput for each sport. In this case, the total throughput of the bath should not exceed the allowable one according to SanPiN 2.1.2.1188.
5.41 For training sessions, a sports bath can be divided into a larger number of tracks based on the reduced width of the tracks (subject to the presence of embedded elements in the walls of the pools for attaching cables) with a larger total capacity of the bath, but not more than allowed by SanPiN 2.1.2.1188.
5.42 Direction indicators (cords with flags) for swimming on the back are installed on vertical posts (in mounting cups on the sides of the pool). Racks provide fixing of the pointer across the bath 5 m from each end wall at a height of 1.8 m from the water surface.
5.43 The false start cord is installed on vertical posts (in the mounting cups on the sides of the pool). Racks provide fixation of the cord across the bath 15 m from the starting block at a height of at least 1.2 m above the water level. The cord must be a quick release mechanism and must cover all lanes when dropped into the water. The need for a cord is determined by the design task.
5.44 Embedded parts used for fastening the racks of the false start cord and the cord with signal flags are placed on the bypass path behind the overflow chute.
5.45 The color of the axes of the tracks on the bottom of the bath should be in contrast to the color of the bath coating. The markings for 50- and 25-meter swimming baths are shown in figures 5.7, 5.8 and 5.9.
5.46 All sides of the sports pool baths must have an overflow chute, which must be covered with a special grate. When designing overflow type baths, one should take into account the need to install rotary shields on the end walls of the pool, protruding to a height of 0.3 m above the water surface.
5.47 When designing multifunctional pool baths, a floating partition (movable starting block) is provided - it serves to imitate the end wall of the pool and must completely cover the pool. The partition must be stable, with a smooth non-slip surface on which starting bollards, contact panels can be installed, lowered at least 0.8 m below the water level in the pool and protruding 0.3 m above its level. There should be no holes or crevices in the partition, which could accidentally get the fingers of the athletes. The design of the partition must ensure the free movement of judges, participants and service personnel along it, which does not cause movement of water in the pool and does not create turbulence.
In pools with a movable baffle, the length of the pool bath must be determined taking into account the thickness of the baffle in it.
5.48 Along the walls of the swimming pool at a depth of not more than 1.2 m from the water surface, a ledge for recreation with a width of 0.1 to 0.15 m should be provided. In universal and specialized baths for jumping into the water, along the wall along which the jumping devices are located, gentle steps are arranged to exit the water, a ledge for rest is not provided (see Figure 5.12).
5.49 Dividing paths are stretched along the entire length of the pool and fixed on the end walls with anchor bolts or other embedded devices. Anchor bolts (embedded devices) must be attached to the walls of the pool in such a way that the ends of the dividing cords near the walls of the pool are at the level of the water surface. The track consists of wave absorbers and floats (elements) tightly strung on a cord with a diameter of 0.1 m to 0.15 m. The color of the elements at the two five-meter ends of the track should be red (see Figure 5.7A), the color of the elements in the central part (see .figure 5.7B) should be:
green - for separating cords between the bathtub wall and edge tracks;
yellow - for dividing cords separating the central tracks;
blue - for dividing cords between other tracks.
Separation cords must be tightly stretched.
Bath dividing lanes 25 m long must have a 15 m mark at both ends (float in contrasting color). In 50-meter pools, the 25-meter distance mark must also be marked with a special color float.
5.50 In bathtubs for sports swimming, one or both end walls should be provided with starting bollards.
Starting bollards, height above water level from 0.5 to 0.75 m, must be made of solid material (without springy effect). Dimensions of the non-slip surface of the starting bollard - not less than 0.5x0.5 m, the maximum angle of inclination of the bollard surface can be no more than 10 °. The design of the starting pedestal can be provided with an adjustable stop for pushing off with the legs and handrails for gripping with the hands. To start, when swimming on your back, vertical and horizontal handrails must be installed at a height of 0.3 to 0.6 m above the water surface in both horizontal and vertical planes.
5.51 Embedding devices should not protrude from the plane of the walls of the bath and the bypass path.
5.52 All baths should be provided with ladders for entry/exit from the water. A bathtub for sports swimming 50 m long should be equipped with three ladders on each long side, a bathtub 25 m long - two ladders located in niches that do not protrude from the plane of the walls of the bathtubs.
The dimensions of the niche must be provided in accordance with the dimensions of the stairs:
0, 8-1x0, 2-0, 25 m - the size of niches for stairs in the plan;
The handrails of the stairs are made of different heights for convenient use by visitors of different heights;
Stairs must be made of stainless steel;
Ladder width - 0.6 m, distance between steps - 0.3 m;
Stairs are located no closer than 3 and no further than 5 m from the end walls; in the case of the installation of viewing windows or outflows, they are placed further from the end wall than the viewing window or outflow;
Pools for synchronized swimming
5.53 The layout of the competition area for synchronized swimming in a 50-meter swimming pool is shown in Figure 5.10. For competitions in compulsory and free programs, the sports area of the category A pool bath must be 20x30 m and 3 m deep. The capacity of the bath for synchronized swimming should be taken according to the maximum number of participants - 10.
For free programs, the minimum competition area is 12x25 m.
For the disciplines of synchronized swimming Solo and Duet, the competition area must be 16x25 m in size.
If there are no marking lines for sports swimming on the walls of the pool, contrasting lines should be applied longitudinally to the bottom of the pool.

5.54 The minimum height of the starting platform for synchronized swimming is 0.5 m, preferably 0.7 m.
5.55 The height of the platform for judges is 0.6 m.
Water polo pools
5.56 The layout of the competition area for water polo in a 50-meter swimming pool is shown in Figure 5.11.


5.57 The distance between the goal lines for water polo shall be 30 m for men and 25 m for women. The boundary of the playing area at both ends is at a distance of 0.3 m behind the goal line. The width of the playing field is 20 m. The depth of the pool is at least 1.8 m, preferably 2 m.
5.58 On both sides of the playing area (playing field) for water polo, clear markings should be provided to indicate the goal lines, the line 2 m and 5 m long from the goal line and the line of the middle distance between the goal lines. The white line is measured from the border of the playing field and is located at a distance of 0.3 m from the goal line, it is carried out from both sides of the field. The 2m red line is measured from the end of the goal line and runs from both sides of the field. The yellow line is 3m long from the 2m line and runs from both sides of the field. The middle section of the playing field must be green, for games of men's teams it must be 20 m, for games of women's teams - 15 m. In the middle of the green zone, it is applied white line markings to indicate the center of the field. Zones for replacing players are located in two corners on the sides on the opposite side of the pool from the referee's table. They are 2 m long and run along the goal line.
In the center of the field, at the bottom of the bath, a device for releasing the ball is installed.
5.59 Platforms 1 m wide and 0.7 m high above the water level must be arranged on both sides of the playing field. They are designed for the free movement of referees from one end of the playing field to the other.
5.60 The capacity of category A baths for water polo should be taken from the calculation of the composition of two teams - 14 people.
Diving pools
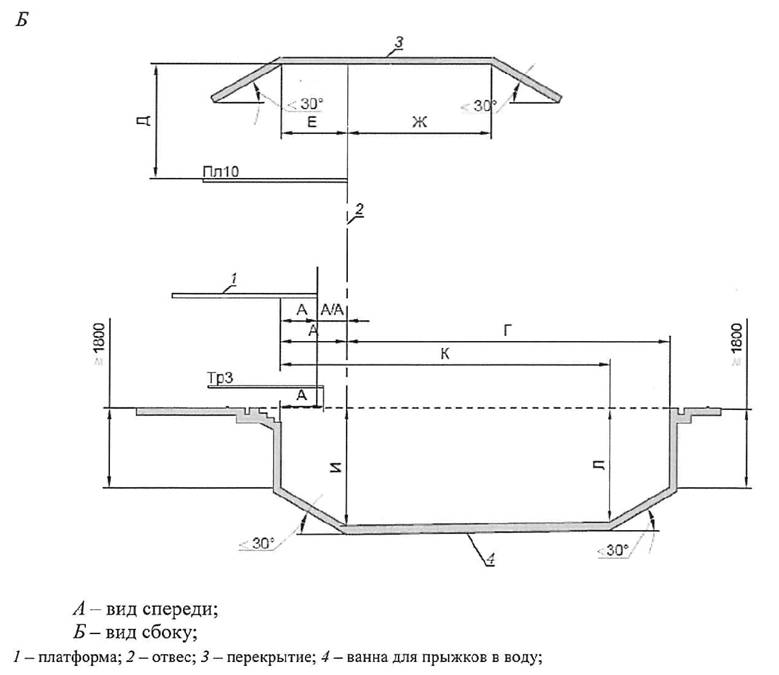
5.61 Dimensions of diving baths and placement of jumping devices (springboards and platforms) should be taken in accordance with those shown in Figures 5.12, 5.13.
The error in the installation of springboards and platforms above the water level should not be more than plus 50 mm.

Parameters and dimensions of springboards and diving platforms



5.62 The size of the side of specialized baths for jumping, where jumping devices are installed, is recommended to be taken equal to 25 m in order to be able to use them for swimmers.
5.63 The capacity of each jumping device is assumed to be 6 people. per shift, the maximum capacity of a specialized diving bath with complete set jumping devices are accepted in 30 people.
5.64 In places where springboards are installed, if necessary, embedded parts for their fastening should be provided.
5.65 The jumping board must be at least 4.8 m long and 0.5 m wide, with a non-slip surface, a rigidly fixed end and a movable support that can easily change the damping characteristics of the board.
5.66 For springboards on a concrete platform, the following requirements must be met:
The height from the top of the platform supporting the frame to the top of the springboard should be 0.35 m;
The distance from the front edge of the bed to the front edge of the platform should be no more than 0.44 m (bed length 0.741 m);
5.67 The front edges of springboards of the same height must be in line.
5.68 Springboards are placed on one or both sides of the platforms. For the program of synchronized diving competitions, it is necessary that at least two springboards of the same height be located on a common platform (increased width) or on adjacent supports.
5.69 The diving platform must be rigid and level.
5.70 The minimum dimensions of jumping platforms are given in Appendix B.
On a 10 m platform with a width of less than 3 m, a fence must be installed. The railing should end at a distance of 3 m from the front edge of the platform. It is allowed to use removable sections of the fence (closest to the front edge) on the 10 m platform for the execution of synchronized jumps.
5.71 The thickness of the front edge of the platform should be 0.2-0.3 m.
Platforms must be non-slip, suitable for dry, wet or wet conditions.
5.72 The projection of the front edge of the platform 10 m should protrude forward beyond the projection of the bath wall by at least 1.5 m; platforms 7.5 m, 5 m and 2.6-3.0 m - by 1.25 m; platforms 0.6-1.0 m - by 0.75 m.
When two platforms are located directly below each other, the upper platform must protrude a minimum of 0.75 m (preferably 1.25 m) beyond the edge of the lower platform.
5.73 Platforms with a height of 1 m or more must be fenced on the sides and rear edge. The minimum height of the fence should be 1.0 m with vertical supports every 1.8 m and two horizontal lintels between them. The railing is installed along the outer plumb lines of the platform and ends at a distance of 1 m from the front edge. The layout of the platform fencing is shown in Figure 5.13A.
5.74 Each platform should be equipped with a lifting device or ladder.
5.75 The design load from the platforms and springboard support devices on the support part of the tower is 350 kgf/m 2 .
For the safety of the user, the following restrictions regarding platforms and springboard supports must be observed:
Natural oscillation frequency of platforms - no more than 10 Hz;
Natural frequency of the tower - no more than 3.5 Hz;
The fluctuation of the whole structure is no more than 3.5 Hz.
The deformation of the front edge of the platform under the influence of a load of 100 kg should not exceed 1 mm.
5.76 In bathtubs for jumping into the water and in the deep part of universal bathtubs intended for jumping, the bottom slope should be taken according to Figure 5.12.
5.77 The edges of the 5m, 3m and 1m platforms must not protrude beyond the edge of the 3m and 1m springboards when placed side by side.
5.78 Sports baths for diving must be equipped with a device for creating wave ripples on the surface of the water. To achieve the goal, it is allowed to use any mechanism for creating wave ripples: bubble (air cushion) or jet (horizontal spray).
On the bypass paths of baths for jumping into the water and universal baths, in close proximity to the jumping devices, shower installations should be located at the rate of one net per 10 jumpers. The shower can be located in open cabins or without cabins. Water temperature - 36°С - 40°С.
5.80 The width of the marking lines for jumping pools should be 0.2 m, but not more than 0.3 m, length: 21 m for a 25-meter pool length (see Figure 5.13B).
In specialized baths for jumping into the water, one ladder or steps are allowed to exit the water, located under the jumping devices along the entire width of the bath (see Figure 5.12, sheet 1).
5.81 In the buildings of sports pools, places for spectators are located outside the sports area and the evacuation passage, if evacuation is provided for along the aisle in front of the first row of spectator seats, the number of continuously installed seats in a row should be no more than 26 with a one-way exit from the row, no more 50 - with a two-way exit.
5.82 Seats for spectators on balconies are allowed in swimming pools. The balcony is arranged along the longitudinal walls of the hall, should not interfere with the placement under it sports equipment.
5.83 The depth of a row on stationary stands is 0.9 m. On transformable stands, this size may be reduced to 0.8 m.
The minimum width of the seat is 0.45 m, the recommended width is 0.5 m.
The seating depth in stationary stands is 0.4 m. In transformable stands, it can be reduced to 0.35 m.
5.84 Visibility conditions are given in .
5.86 The slope of the grandstand stairs for spectators is determined according to SP 118.13330.
5.87 Seats in the stands for people in wheelchairs, their attendants and other categories of people with limited mobility are designed in accordance with SP 59.13330.
5.88 When calculating the auxiliary premises of pools with spectator seats, the number of spectators should be taken into account when calculating the area:
Vestibule (additionally 0.25 m2 per seat);
Wardrobe (additionally 0.1 m 2 per seat, but not less than 10 m 2);
Foyer (additionally 0.35 m2 per seat);
Dining room, buffet (additionally 1.4 m 2 per seat);
Additional sanitary facilities, based on the number of spectators in accordance with SP 118.13330.
5.89 In sports pools intended for holding all-Union and international competitions rooms for judges and a press center are provided. They include: the chief judge's office - 10-12 m 2 ; room panel of judges 16-20 m 2; secretariat room - 16-20 m 2; a room for multiplying equipment - 10-12 m 2.
5.90 As part of the pool premises, a hall is provided for awarding winners and prize-winners, an engraver's workroom - 8 m 2, a pantry for storing prizes - 6-8 m 2.
5.91 The composition of the premises of the press center is determined by the design assignment.
bypass paths
5.92 Along the perimeter of the baths, a bypass path should be provided with a width of at least 2 m for indoor baths and at least 2.5 m for open baths (counting from the outer edge of the bath wall).
The width of the bypass path at the end wall of the bathtub with starting tables is taken at least 3 m; the width of the bypass track along the walls with jumping devices is taken taking into account the dimensions of these devices and the provision of approaches to them.
The surface of the walkway must be non-slip with a slope of 0.01-0.02 towards the ladders.
Along the outer perimeter of the bypass paths of open baths, a stationary fence should be provided to prevent unauthorized persons from accessing the baths.
6 Dressing rooms
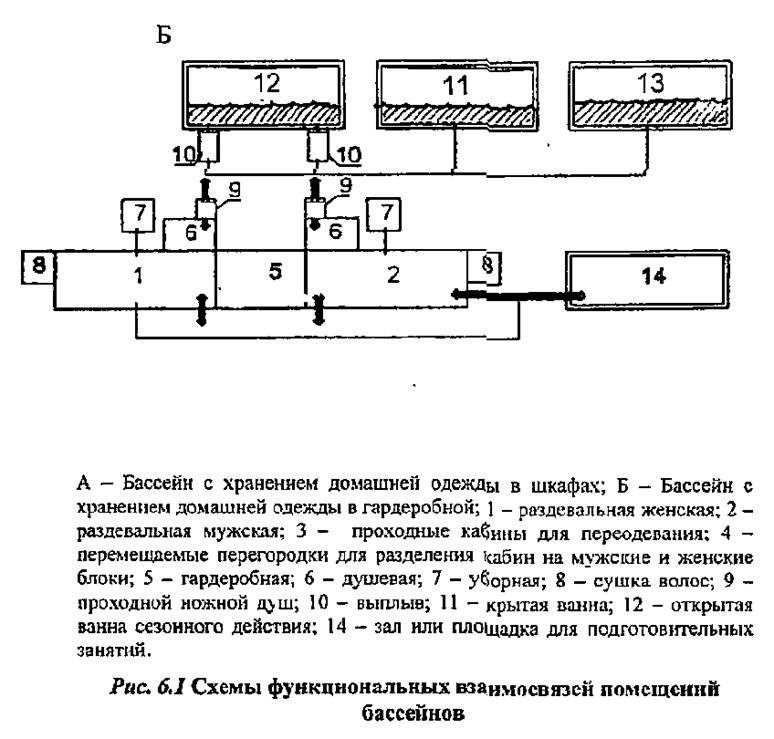
6.1 The dressing rooms are located at the same level with the bypass paths around the pool baths and communicate with them through the showers, and with the hall or platform for preparatory classes- bypassing the showers. The functional relationships of the changing rooms and the pool are shown in Figure 6.1.

6.2 In pools with several baths, it is recommended to design separate dressing rooms for each of them.
6.3 The number of places in the locker room is taken equal to the number of students in one shift. The ratio of seats in the men's and women's locker rooms is assumed to be 1:1, unless otherwise provided by the design assignment.
6.4 Dressing rooms are intended both for changing clothes and for storing clothes.
6.5 For changing clothes in the locker rooms, benches are arranged at the rate of 0.6 m of bench length per one seat. The area of one dressing room (taking into account the approach to it) is: if the number of places in the dressing room is less than 40 - 1.5 m 2, if the number of places in the dressing room is more than 40 - 1.2 m 2.
6.6 Storage of clothes is provided in closed cabinets of two types: two-tier (each cabinet for two places) and single-tier (each cabinet for 3 places).
6.7 For older students and adults, for one place on the bench for changing clothes in the locker rooms, the following should be provided:
Three places in cabinets in pools without a hall for preparatory classes for swimmers;
Five places in the lockers in the pools with a preparatory room.
6.8 In swimming pools for preschool children, only single-tier wardrobes are provided in the locker rooms, while three places for storing clothes (one single-tier wardrobe) are provided for one changing place.
6.9 The total area of the dressing rooms per student is:
for dressing rooms with up to 40 seats:
2, 1 m 2 - in pools without halls for preparatory classes;
2.5 m 2 - in pools with halls for preparatory classes;
for dressing rooms with 40 seats or more:
1, 7 m 2 - in pools without halls for preparatory classes;
2, 1 m 2 - in pools with halls for preparatory classes.
for locker rooms intended for children under 10 years old - 2.9 m 2.
6.10 The width of the passages between the elements of equipment in the locker rooms is given in Appendix D.
6.11 Showers at the dressing rooms are designed on the basis of one shower net for three people simultaneously engaged in the bath.
For shower rooms with more than six grids, an entrance hall is provided, the area of \u200b\u200bwhich is determined at the rate of 0.3-0.5 m 2 per shower grid. The entrance hall is equipped with towel racks and cells for storing soap and washcloths.
6.12 At the exit from the shower room to the bypass path, a walk-through foot shower is provided with a length (in the direction of movement from the shower room) of at least 1.8 m, a depth of 0.1-0.15 m. A foot bath may not be provided for direct exit from the shower room to the bypass pool path.
6.13 In the locker rooms, foot washing should be provided at the rate of one wash for 20 changing places, but not less than one.
6.14 Hair dryers are installed in the locker rooms or adjacent premises at the rate of one dryer for 10 places for changing clothes in the women's locker rooms and one dryer for 20 places - in the men's locker rooms. To place the dryers, an additional area is provided at the rate of 1.3 m 2 per dryer.
6.15 Restrooms for students should be located at the locker rooms, while the possibility of passing through the restrooms to the bath, bypassing the showers, is excluded.
6.16 It is not allowed to place latrines and showers above the premises for the preparation and storage of coagulating and disinfecting solutions.
6.17 The estimated number of sanitary appliances is given in Appendix D.
6.18 For citizens with limited mobility, changing rooms should be provided in showers and changing rooms. Cabin layouts are shown in Figure 6.2.

7 Ancillary facilities
7.1 Auxiliary facilities of the pools are divided into mandatory and recommended. Their composition is given in Appendix E.
7.2 As a rule, spectator seats are not provided for sports and recreation pools.
7.3 In swimming pools located in separate buildings, the area of the dressing room of the outerwear of those involved is determined at the rate of 0.1 m 2 per place, but not less than 10 m 2.
7.4 In preschool and educational organizations with swimming pools, the number of places (hooks) should be increased by:
200% of the number of children involved in the pool at the same time - taking into account pools with halls for preparatory classes;
100% of the number of children simultaneously involved in the pool - taking into account pools without halls for preparatory classes;
7.5 The number of hooks in the wardrobe of employees of an educational organization with a pool should be increased by the number of pool employees determined by the staffing table. For employees involved in the pool, a separate wardrobe can be designed.
7.6 In health-improving pools where paid services are provided, a reception room with an area of at least 6 m 2 and a cash desk area of at least 4 m 2 should be designed with access to the lobby of the building.
7.7 The premises of swimming teachers (instructors) are designed at the rate of 2.5 m2 per teacher, but not less than 10 m2. It is equipped with a separate shower, toilet and changing cabins. Instructors' quarters are provided, as a rule, separate for men and women.
In addition to the common room for instructors in training and health pools, an 8 m 2 room for an instructor on duty should be designed - which should have access to the pool bypass. The presence of this room does not reduce the required capacity of the instructors' common room.
7.8 Halls for preparatory classes are designed near the baths of the pools, and it is recommended to provide for each bath its own hall. The area of the hall, regardless of the age of those involved, is taken at the rate of 11.5 m 2 per one involved in the pool.
7.9 In the buildings of educational organizations, it is recommended to place the halls of the preparatory classes of the pool together with other sports halls in the same area of the building.
7.10 Halls of preparatory classes are equipped with inventory rooms with an open doorway with a width of at least 1.8 m.
7.11 In educational and recreational pools, a room for a nurse on duty with an area of 12 m 2 is designed, with direct access to the bypass path of the pool bath. With several baths located in different rooms, a nurse's room is provided for each bath.
7.12 The study room is designed with an area of 40 m 2 . In a pool with several baths, according to the design assignment, two teaching and methodological rooms can be provided.
7.13 The composition and area of the administrative and utility rooms of the pools should be determined according to SP 118.13330 and GOST R 53491.1.
7.14 When placing a pool on the area of an educational organization or a multifunctional sports and recreation center, the composition of the pool premises should be determined as part of their general composition in the organization (institution), excluding duplication.
7.15 The composition, area and height of the technical premises depend on the engineering decisions made and are determined by the design assignment.
7.16 The premises of the chlorination room (8-10 m 2) and the chlorine warehouse (6 m 2) for storing no more than two filled cylinders with a capacity of 40 kg each may be placed at the outer wall of the pool building, above ground level, with separation from other premises by enclosing structures made of fireproof materials with a fire resistance limit of at least 0.75 h.
The premises of the chlorination room and chlorine storage should be with access to the street directly or through the vestibule. It is allowed to arrange a common vestibule for exiting from both rooms to the outside.
It is not allowed to have sanitary units and showers above the premises for the preparation of disinfectant and coagulating solutions.
7.17 In the swimming pool buildings, as part of the auxiliary premises, a chemical laboratory room with an area of 18 m 2 equipped with hot and cold water inlets, a fume hood in accordance with GOST R 53491.1 should be provided.
7.18 It is allowed to include a medical rehabilitation center in the pool premises (Appendix G). The need for its inclusion is determined by the design task.
8 Structures and decoration of rooms with damp and wet conditions
8.1 When designing reinforced concrete and steel structures of pools, they should be protected from corrosion in accordance with SP 28.13330, when designing wooden structures, measures should be taken to ensure their durability in accordance with SP 64.13330.
8.3 The internal surfaces of the enclosing structures of the premises must be free of protrusions and places of possible accumulation of moisture and dust. The junctions of walls and columns with the floors of rooms with damp and wet conditions should be rounded.
8.4 On inner sides Enclosing structures of rooms with wet and wet conditions, in accordance with the calculation, should be vapor barrier or waterproofing made of bioresistant materials.
8.5 In the interfloor ceilings and floors of the first floor of rooms with wet and damp conditions, waterproofing should be provided. Waterproofing should be installed on the wall, partitions and columns 300 mm above the floor surface.
Joints between prefabricated floor elements must be with an additional layer of waterproofing 100 mm in each direction.
8.6 Walls and partitions in rooms with wet and damp conditions should be lined with ceramic, polymer or glass tiles to the full height. Wall cladding is allowed to a height of 1.8 m from the floor level, above - painting with waterproof paints. For interior decoration, light-colored materials should be provided.
8.7 Floors in rooms with damp and wet conditions must be resistant to moisture and disinfectant alkaline solutions, easy to clean from contamination.
In rooms with a wet regime, the level of the finished floor should be 30 mm lower than the floor level of other adjacent rooms, the floor surface should be non-slip.
Reinforced concrete structures covered with tiles, PVC film or elastic material that meet the requirements of Rospotrebnadzor;
Metal welded structures made of stainless steel;
Metal prefabricated structures laminated with PVC film;
Metal prefabricated structures covered with PVC film.
8.9 Bypass paths and sides of the bath are lined with ceramic, concrete or mosaic slabs with a rough, non-slip, possibly corrugated surface.
8.10 The coating material of the walkway, benches, walls and bottom of the baths must be resistant to chemicals used for water and bath purification and easy to clean and disinfect. The inner surface of the walls and bottom of the baths is made of light-colored materials. The seams between the facing tiles are rubbed.
8.11 Filling of window and door openings in rooms with damp and wet conditions should be made of water-resistant and bio-resistant materials. It is allowed to provide window casings made of antiseptic coniferous wood, protected from moisture by moisture-resistant coatings.
8.12 To ventilate the premises in window frames, it is necessary to provide for opening transoms or vents located in the upper part of the openings. Transoms and vents must be isolated from the inter-window space with special boxes.
9 Natural light
9.1 Bath rooms and preparatory rooms should have direct natural light. The area of light openings (% of the floor area of the hall) is:
for bath halls (including water surface area):
14% - 16% - with one-sided side lighting,
12% - 13% - with two and multilateral side lighting;
for preparatory classes:
17% - with one-sided side lighting;
14% - with two and multilateral side lighting.
9.2 Wall and ceiling light openings to ensure uniform lighting are recommended to be designed as tape and placed at least 2 m from the level of the bypass path.
9.3 The orientation of the light openings in the bath rooms and halls for preparatory classes is not regulated.
9.4 Natural lighting in the buildings of sports and recreation pools is provided for the nurse's office, teaching and methodological office, workshops, administrative premises, engineering and technical staff premises, fire station, security, sports equipment warehouses, utility storerooms. In other rooms, the need for natural lighting is determined by SP 52.13330 and SP 118.13330.
10 Water supply and sewerage
10.1 If there is no centralized water supply in the settlement, to provide pools with water, it is planned to install its own water intake unit or use local sources, the water in which must comply with SanPiN. 2.1.4.1074, GOST R 53491.1 and GOST R 53491.2.
10.2 For seawater pools, the choice of the water intake site should be carried out in accordance with 10.1. In this case, the head of the water intake should be at a height of at least 2 m from the bottom surface with a supply sea water from the middle layers.
10.3 The quality of water entering the baths of sports and recreational pools must comply with SanPiN 2.1.2.1188 and GOST R 53491.1.
10.4 The arrangement of internal drinking water and fire-fighting water pipes, water consumption rates per day, hours of maximum water consumption, and sewerage are given in and must comply with SP 30.13330.
10.5 Water consumption for washing bypass paths, as well as for staff and in cafeterias, is taken into account separately.
The calculation of water consumption in buffets can be performed both by the number of served dishes and by the number of washes.
10.6 Pass-through foot showers should be provided with a continuous flow of water.
10.7 To meet household and technological needs, hot water supply should be provided.
10.8 Hot water consumption should be determined in accordance with SP 30.13330.
Separately, it is necessary to take into account the cost of hot water for a walk-through foot shower with a flow rate of 720 l / h, a temperature of 30 ° C - 35 ° C, a duration of 30 minutes per shift and washing bypass paths and showers with a flow rate of 6 l / m and a temperature of 30 ° C (twice a day).
10.9 Hot water supply should be provided for showers, a doctor's office, a nurse's room, amenity rooms for workers, locker rooms for trainees, instructors' rooms, buffets, a water analysis laboratory, rooms for cleaning equipment, as well as other rooms in accordance with the technological task.
10.10 In sanitary facilities and shower rooms with more than two devices (toilet bowls, urinals, shower nets) and on the bypass paths of the baths, installation of watering taps with a diameter of 20 mm with cold and hot water supply should be provided. Watering taps of open baths should be installed in heated rooms.
10.11 At the pool baths, it is allowed to arrange drinking fountains for students, installed within the bypass path.
30°С - 32°С - for preschool children;
29°С - 30°С - training;
26°С - 29°С - wellness;
25°С - 28°С - for sports swimming;
Not less than (27±1)°С - for synchronized swimming;
Not less than (26±1)°С - for water polo;
At least 26°C - for diving,
in accordance with SanPiN 2.1.2.1188.
10.13 Swimming pools must be equipped with systems that provide water exchange in the pool baths. According to the principle of water exchange, pools are divided into:
Recirculation (reverse) type;
flow type;
With periodic water changes.
10.14 For baths of preschool children, the principle of recirculation with periodic water changes is recommended. For bathtubs of educational, improving and sports pools - water exchange of reverse type is recommended.
10.15 Recirculation in pool baths provides for the repeated use of water with purification, disinfection and simultaneous replenishment of waste with fresh tap water in accordance with SanPiN 2.1.2.1188.
Not more than 0.5 hours - for pools of preschool children;
No more than 4.0 h - for training pools;
No more than 6.0 hours - for health pools;
No more than 8 hours - for sports pools.
The specified time for complete water exchange does not apply to flow-type pools.
10.17 Water supply to pool baths can be carried out through holes in the walls and bottom of the baths (the second option is preferable), the location of which should ensure its uniform distribution throughout the volume to maintain its temperature constant, as well as uniform distribution of the disinfectant.
The rate of water exit from the supply holes should be taken no more than 2-3 m 3 / s.
10.18 For flow-type pools and with water change, it is allowed to use water coming from a centralized drinking water supply system, subject to the requirements of SanPiN 2.1.2.1188. The need for disinfection of such water is determined by GOST R 53491.1.
10.19 Purification of process water in pool baths should be carried out in accordance with SanPiN 2.1.2.1188.
10.20 Drainage facilities in pools should be provided separately for each bath or for a group of baths of the same purpose.
10.21 Sequential inclusion of two or more baths into a single water treatment system is not allowed.
10.22 Disinfection of water in pools should be carried out in accordance with GOST R 53491.1 and SanPiN 2.1.2.1188.
10.23 On process pipelines in pools, installation should be provided for:
Flow meters showing the amount of water supplied to the bath;
Flow meters showing the amount of fresh tap water entering the recirculation system;
Control taps for water sampling:
Incoming to the water treatment system of pools of all types;
Before and after filters - in recirculating pools;
After disinfection before supplying water to the bath.
10.24 For pumping and filtering units located below the surface of the water in the baths, check valves should be installed on the process pipelines supplying water to prevent water from draining from the baths into the technical rooms in case of depressurization flange connections fittings and equipment.
10.25 When water is taken from overflow gutters for recirculation, its allowable volume from the total recirculation water flow is determined by GOST R 53491.1.
To store water from the overflow gutters, an accumulator tank (balance tank) is installed. Renewal of water in the pool is carried out continuously during the day in accordance with GOST R 53491.1.
10.26 To reduce the total water consumption for technological needs, water from the balance tank can be used (irrigation, cleaning of premises, etc.).
10.27 Losses of water for evaporation, entrainment and splashing Q, m 3 / h, in covered baths can be determined on an aggregate basis by the formulas:
in all baths, except for baths for teaching non-swimmers:
Q=0.0064F; q h =0, 0003F;
in swimming baths:
Q=0.0083F; q h =0, 0004F;
where F is the area of the water mirror, m 2.
10.28 Water consumption, m 3 /day, used for washing filters, is determined according to GOST R 53491.1.
10.29 Water consumption Q 2, m 3 / day, for washing bypass paths and showers with a bath is determined by the formula (two cleanings per day): Q 2 \u003d 0.012F d,
where F d is the area of the premises to be cleaned, m 2.
10.30 Discharge of water from walk-through foot showers, from bypass paths and from washing the walls and bottom of the pool baths should be provided for in the domestic sewer.
10.31 Water from drinking fountains or drinking machines, emptying bathtubs, washing filters should be discharged into the rain sewer.
10.32 The duration of the water flow when emptying pool baths with a volume of 600 m 3 or less should be taken no more than 12 hours, and with a water volume of more than 600 m 3 - no more than 24 hours.
10.33 The design of water supply and sewerage systems for pool buildings must comply with SP 30.13330.
11 Heating and ventilation
11.1 The heating and ventilation systems of swimming pools must provide the values of the microclimate and air exchange parameters of the swimming pool rooms, given in Appendix I.
11.2 Air mobility in the areas where trainees are located should not exceed:
0.2 m 3 / s - in the halls of the baths of the pools;
0.5 m 3 / s - in the halls for preparatory classes.
50% - 65 - in the halls of the pool baths;
30% - 60% - in the halls for preparatory classes.
11.4 In the course of thermotechnical calculation of the enclosing structures of the pool halls, the relative humidity of the air should be taken as 67%, and its temperature - 1°C - 2°C higher than the water temperature in the pool.
11.5 Heating appliances and pipelines in the halls of pool baths and halls for preparatory classes, when they are installed at a height of up to 2 m from the floor, should not protrude from the plane of the walls.
11.6 Bypass paths and stationary pool benches must be heated.
11.7 Separate supply and exhaust ventilation systems should be provided for:
Halls of pool baths;
Halls for preparatory classes;
Premises for administrative and engineering personnel, amenity premises for workers;
Chlorine and chlorine warehouses;
Technical premises (pump-filtering, boiler, ozonation, etc.).
Panels for turning on ventilation systems serving the chlorinator and ozonator should be installed outside these premises.
11.8 For bath halls, it is recommended to use ventilation units operating in two modes: independent supply and exhaust units designed only for the non-working period of the pools; additional installations, together with the first two, should, during the operation of the pools, provide the calculated air exchange.
11.9 Removal of air from the halls of pool baths should, as a rule, be provided by mechanically driven exhaust systems; in the halls of preparatory classes, it is allowed to use systems with natural stimulation, using ventilation shafts installed on the roof of the building.
11.10 Exhaust ventilation systems from sanitary facilities and from showers may be combined.
11.11 In the halls of baths and preparatory classes, combined air heating systems combined with air ventilation can be used. In these systems, the principle of air recirculation is allowed. In this case, the volume of supplied outside air must not be less than that specified in Appendix K.
11.13 When the outside air temperature is below minus 20°C, it is recommended to install thermal air curtains in the vestibules of the main entrances of swimming pools. It is allowed to replace the air-thermal curtain with a vestibule with three consecutively located doors.
11.14 Ventilation of chlorination rooms and chlorine stores should be provided for periodic operation. Air is removed from two zones: the upper one in the volume of 1/3 and the lower one - 2/3 of the total volume of the hood. Ventilation units must be placed outside these rooms. The units are controlled from starting devices installed at the entrance to the premises.
11.15 It is recommended to place the premises of the supply systems in the basement or basement floors (on the ground) so that the length of the air duct routes is minimal. In exceptional cases, when it is not possible to place these premises on the lower floors, they may be located outside the main building (in a separate or attached block).
11.16 Heating, ventilation, hot water supply and air conditioning systems in pool buildings should be designed in accordance with SP 60.13330.
12 Power supply and electrical devices
12.1 Artificial lighting is provided in all areas of the pools, as well as in outdoor year-round baths.
12.2 The level of illumination of pool baths is 150 lux on the surface of the water for indoor baths, and 100 lux for open baths.
The lighting intensity for sports swimming on the starter raft and the turning end of the pool must be at least 600 lux. During category A competitions in sports swimming, the illumination of the entire pool must be at least 1500 lux.
Illumination for water polo - at least 600 lux.
Illumination during competitions of category A in water polo and synchronized swimming - at least 1500 lux.
The minimum illumination at a level of 1 m above the water surface in jumping pools must be at least 600 lux, during category A competitions - at least 1500 lux.
12.3 The level of minimum horizontal illumination of the floor surface of the halls and the surface of open areas for preparatory classes should be taken as 150 and 50 lux, respectively.
12.4 As a rule, gas-discharge lamps should be used for lighting recreational and training pools. In this case, the maximum allowable pulsation coefficient of illumination should not exceed 15%.
12.5 If it is necessary to smoothly control the luminous flux and in cases where it is impossible to use gas-discharge light sources, it is allowed, and at illumination levels of less than 30 lux, it is recommended to use incandescent lamps.
12.6 In swimming pool buildings, evacuation lighting should be provided in accordance with SP 52.13330. At the same time, emergency illumination of at least 5 lux must be provided on the surface of the water in indoor pools, as well as outdoor pools equipped with lighting installations.
To illuminate halls with a height of 8 m or less, it is recommended to use an upper-side lighting system with the installation of lamps on the side walls and ceiling outside the water surface. The most comfortable lighting system is the reflected light system. When installing fixtures on the ceiling of the hall, it is necessary to ensure a deviation angle of at least 40 ° in the longitudinal and transverse planes.
12.7 In case of upper-side lighting of halls with direct light fixtures of concentrated light distribution, the inclination of the optical axis of the fixture should be no more than 40° to the vertical.
12.8 When the fixtures are located above the water mirror, the lighting fixtures are installed on special walkways located under the ceiling parallel to the longitudinal axis of the bath. The arrangement of lighting fixtures on the walkways should ensure uniform illumination of the water mirror when the optical axis of the spotlight deviates from the vertical by no more than 45 °.
12.9 The inclination of floodlights with concentrated light distribution shall not exceed 40°.
12.10 With upper or side lighting of the bath halls and preparatory classes, at least 10% of the total luminous flux of lighting fixtures is directed upwards to illuminate the ceiling.
12.11 To limit the glare of luminaires when illuminating halls, the glare index should not exceed 60.
When using gas-discharge lamps, lighting control is carried out in three or four steps.
12.12 On illuminated outdoor pools, upper-side lighting should be provided. Lighting devices of upper-side lighting are installed at a height of at least 10 m, providing the condition according to which the perpendicular, lowered from the optical center of the device to the longitudinal axis of the bath, will make an angle of at least 27 ° with its surface.
When using floodlight masts, they are placed along the longitudinal sides of the bath.
12.13 On the territory and in the buildings of the pools, the following should be provided:
Radiofication from the radio broadcasting network of the settlement;
Telephonization from the automatic telephone exchange of the settlement;
Electric clock.
12.14 The location of the sound equipment (announcer) room in the indoor pools should ensure visibility of the bath hall. The area of the announcer's room is accepted in accordance with SP 133.13330.
12.15 Natural and artificial lighting should be designed in accordance with SP 52.13330, SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278 and SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1076.
12.16 The electrical equipment of pool buildings should be designed in accordance with and.
12.17 The design of security fire and alarm systems and communications must comply with SP 5.13130, and.
12.18 Requirements and standards for the design of video surveillance systems and access control to pool buildings are given in.
12.19 Measures for lightning protection of pool buildings are given in.
12.20 Pool buildings should be designed in accordance with.
12.21 The requirements for operational and structural safety of design solutions for pool buildings are given in.
13 Acoustics
13.1 In the bath and preparatory rooms, the reverberation time at frequencies of 500-2000 Hz should be taken within the band shown in the graph in Figure 13.1. At frequencies below 500 Hz, the reverberation time can be increased by 15% - 20%.

13.2 Calculation of the acoustic improvement of the pool halls and preparatory classes, sound pressure levels and equivalent sound levels, dBA, should be carried out according to SP 51.13330.
13.3 To prevent the influence of external sources of noise, it is recommended to locate rest rooms for students, teaching and methodological classes, rooms for medical care at a distance from ventilation chambers, pumping stations and other sources of noise.
13.5 When designing halls with convex (dome, vaulted, arched) coverings, in order to avoid concentrations of reflected sound energy and sound focusing, it is recommended to take the radius of curvature of the covering at least twice as large as the height of the pool hall.
14 Automatic and sound equipment of pool baths
14.1 Automatic equipment of pool baths is intended for automation of technologies for conducting sports competitions. When conducting sports and recreation classes, automatic equipment, as a rule, is not used.
14.2 It is recommended to equip the halls of the swimming pool and preparatory classes with devices for broadcasting music and voice messages - for this, a room with an announcer's area of 8-10 m 2 should be provided.
Annex A
Purpose, dimensions and design indicators of recreational swimming pools
Table A.1
|
Types of pools |
For preschool children |
wellness |
|||||
|
Place of application and placement |
preschool educational organizations, children's medical institutions |
educational organizations, children's sanatoriums, recreation camps, sanatoriums, etc. |
places of residence and mass recreation of citizens, sports centers systems of cultural and community services for the population |
||||
|
Purpose |
health improvement and introduction of children to water |
swimming lessons |
sports swimming training | ||||
|
Bath dimensions, m |
25x11 (standard) |
16x11 (shortened) |
arbitrary |
||||
|
Depth, m | |||||||
|
Estimated water surface area, m 2, per person | |||||||
|
* Variant value Notes 1 The pool depth values determine the slope that should be provided along the length of the pool baths. 2 Sizes and shape of sports and health-improving swimming pools are specified by the design task. |
|||||||
Annex B
Parameters and capacity of sports pool baths
Table B.1
|
Purpose of the bath |
Bath size, m |
Water depth in the deep part of the bath, m |
Bath throughput per shift, pers. |
|
|
Swimming |
Based on the slope of the bottom, taken at least 0.01. Depth 1.8 m** | |||
|
Water polo |
At least 33.3 |
At least 21 |
1, 8 (minimum) |
25 (80 for other purposes) |
|
Diving |
30 (max) |
|||
|
* Deviation in the length of bathtubs (including universal ones) is allowed only in the direction of increase within the limits of up to 0.03 m. **Recommended minimum depth for competitive swimming. For category A competitions, the depth is 2.0 m (minimum). The slope of the bottom to the places of water outlet in swimming pools should be taken at least 0.01, but not more than 0.045; slopes in the transverse direction are allowed. *** For competitions of category A of the free program, an area with a minimum size of 30x12 m is required (the depth of the allocated part of 12x12 m is 3 m, the depth of the rest is 2.5 m). Note - In parentheses is the value of the smaller width of the bath and the corresponding throughput. |
||||
Annex B
Diving platform dimensions depending on its height
Table B.1
|
Height above water level, m |
Width, m | |
Annex D
The width of the passages between the elements of equipment in dressing rooms and showers
Table D.1
|
Passages between equipment elements |
Size, m, not less than |
In the dressing rooms |
|
|
Between rows of benches when sitting facing each other | |
|
Between a row of benches and a wall parallel to it or a row of cabinets opposite it | |
|
side aisles | |
|
main passages | |
|
Between rows of wardrobes | |
|
In the showers Between the front of the shower stalls and the opposite wall | |
|
Between the fronts of opposite rows of showers | |
Annex D
Estimated number of sanitary appliances in auxiliary premises
Table E.1
|
Room, sanitary facilities |
Number of sanitary appliances in the room |
Note |
Sanitary facilities for those involved |
||
|
One toilet for 30 changing places, but at least one toilet | ||
|
One toilet and one urinal for 45 changing places, but at least one toilet |
||
Sanitary facilities for employees, instructors and trainers |
||
|
According to SP 118.13330 |
If there are less than 20 men and women working at the same time, a common sanitary unit for one toilet bowl is provided |
|
Other premises and equipment |
||
|
Locker rooms for those involved |
One washbasin for 30 changing places in the dressing room, but not less than one |
Allowed to be placed at restrooms |
|
Rooms for instructors and coaching staff, amenity rooms for workers, nurse rooms of the water analysis laboratory |
One washbasin per room | |
|
Sinks in vestibules of chlorination and chlorine warehouses |
One sink in vestibule | |
|
Washrooms in cleaning equipment rooms |
One car wash per room | |
Appendix E
A set of pool premises according to the criteria of necessity
Table E.1
|
The name of a room |
Pool type |
|||
|
for preschool children |
wellness |
|||
|
exit zone |
||||
|
Lobby | ||||
|
Dressing room outerwear | ||||
|
Security room with video surveillance | ||||
|
Playroom for children | ||||
|
control zone |
||||
|
Registry | ||||
|
Issuance of swimwear | ||||
|
Changing room area |
||||
|
changing rooms | ||||
|
Dressing room for home clothes | ||||
|
Laundry room for bathing accessories | ||||
|
Hair drying room | ||||
|
Sanitary zone |
||||
|
Detergent pantry | ||||
|
Swimming area |
||||
|
Hall with pool baths | ||||
|
shower room with cold water | ||||
|
Staff quarters area |
||||
|
First aid room (nurse on duty) | ||||
|
Duty instructor room | ||||
|
methodical office | ||||
|
Trainer's room (instructors' room) | ||||
|
Service pool staff quarters | ||||
|
Dressing room for staff | ||||
|
Zone of additional premises |
||||
|
Hall of preparatory classes | ||||
|
radio node | ||||
|
massage room | ||||
|
Auxiliary area |
||||
|
Staff rest areas | ||||
|
Storage room for cleaning supplies and equipment | ||||
|
Workshop | ||||
|
Chemical laboratory | ||||
|
Premises for storage of reagents | ||||
|
Designations: "○" - the need for premises is set by the design task; "●" - the need for premises is provided as a rule; "-" - not provided. Notes - The composition of the technical premises, depending on the specific solutions of the engineering systems of the pool buildings, is adopted in accordance with the current regulatory documents. |
||||
Annex G
Composition and areas of the medical rehabilitation center
As part of the premises of swimming pools for health purposes, according to the design assignment, a medical rehabilitation center may be provided.
The premises of the medical rehabilitation center have a separate group, remote from ventilation chambers, pumping and other sources of vibration and noise.
Weight treatment rooms should be with natural light. The width of the corridors of the medical rehabilitation center should be at least 2 m.
The premises of the medical rehabilitation center are recommended to be combined into two blocks:
I - hydrotherapy rooms and a dry heat bath with a contrasting bath and shower;
II - cabinets for electrolight therapy, tests with physical activity, procedural.
A doctor's office and a massage room can adjoin any of these blocks.
Block premises water procedures should be impassable and located as far as possible from the external entrance to the building. The electrolight treatment room should be separated from the hydrotherapy rooms by a "dry" room.
The cabinet of electrolight therapy is equipped with booths 2, 2x1, 8-2 m in size with partitions 2 m high. Each booth is equipped with a couch with a lifting headboard and a device for local lighting and one stationary physiotherapy apparatus. The cabinet must be equipped with an independent ground loop.
The block of water procedures is recommended to be placed on the first floor. The floors of the block premises must be with a slope of at least 0.01 towards the ladder. In the shower room, a shower cabin and shower units fed from it for circular, rain, ascending and jet showers are installed. The shower cabin is installed so that during the jet shower, the patient is at a distance of 3.5-4.0 m from it and direct daylight falls on him. At a height of 1.2-1.5 m, a metal handrail is attached to the wall. Shower installations are equipped in cabins with a plan size of at least 1x1 m, separated by partitions 2 m high, not reaching the floor by 10-15 cm. Shower cabins should be located in such a way that medical personnel can see patients.
The shower cubicle must be supplied with hot and cold water, while the pressure of cold and hot water must be the same (2-2.5 atm.). To maintain constant pressure in the pump room, it is necessary to provide tanks for cold and hot water with a volume of at least 3 m 3 each.
The underwater shower-massage room must be at least 3.5 m wide. The bath with dimensions 2, 33x1, 85x0, 92 (h) must be accessible from three sides. Shower-massage nozzles are located at the end of the bath.
The composition and area of the premises of the center
Table G.1
|
Name of premises |
Area value, m 2 |
|
Doctor's office (head of the center) | |
|
Cabinet of electro- and phototherapy: | |
|
Seven cabins with one daybed each | |
|
Gasket processing room | |
|
Shower room: | |
|
Chair for 5 showers | |
|
Dressing room at the hall | |
|
pumping department | |
|
Underwater shower-massage: | |
|
Bath room | |
|
Cabin for undressing | |
|
A room for carrying out tests with physical activity (veloergometry, spiroergometry, etc.) | |
|
Treatment room for injections | |
|
Lounge (in armchairs) | |
|
Pantry for cleaning items and dirty linen | |
|
staff room | |
|
Toilet: | |
|
Male (one toilet, one urinal with washbasin in the lock) | |
|
Female (two toilet bowls with a washbasin in the gateway) |
Annex I
Air temperature and air exchange rate in pool rooms
Table I.1
|
The name of a room |
Estimated air temperature, °С |
Air exchange rate per 1 hour |
|
|
1 Halls of pool baths |
1°C - 2°C above bath water temperature |
According to the calculation, but not less than 80 m 3 / h of outdoor air per student and not less than 20 m 3 / h per spectator |
|
|
2 Halls for preparatory classes |
According to the calculation, but not less than 80 m 3 / h per student |
||
|
3 Vestibules for students | |||
|
4 Dressing room for outerwear for students and spectators (separated from the lobby) | |||
|
5 Locker rooms |
Similar to showers |
2 (from showers) |
|
Bibliography
Federal Law of July 22, 2008 N 123-FZ "Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements"
Federal Law No. 261-FZ of November 23, 2009 "On Energy Saving and Improving Energy Efficiency and on Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation"
Federal Law of December 30, 2009 N 384-FZ "Technical Regulations on the Safety of Buildings and Structures"
Order of the Ministry of Sports of the Russian Federation of February 25, 2016 N 172 "On approval of the classifier of sports facilities"
SP 31-110-2003 Design and installation of electrical installations of residential and public buildings
Rules for the installation of electrical installations PUE
SO 153-34.21.122-2003 Instructions for lightning protection of buildings, structures and industrial communications
RD 78.35.003-2002 Engineering and technical strength. Technical means protection. Requirements and design standards for the protection of objects from criminal encroachments





